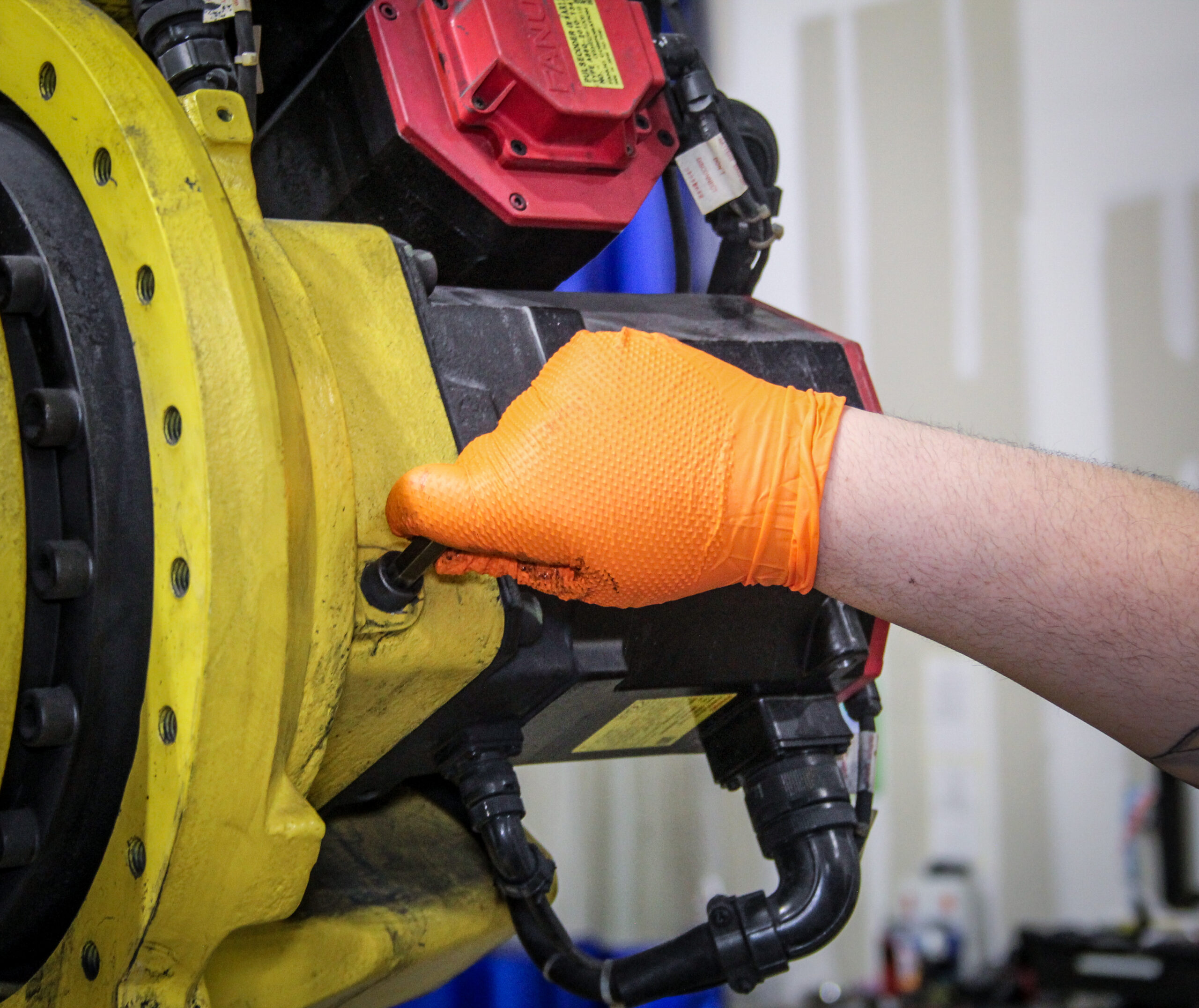
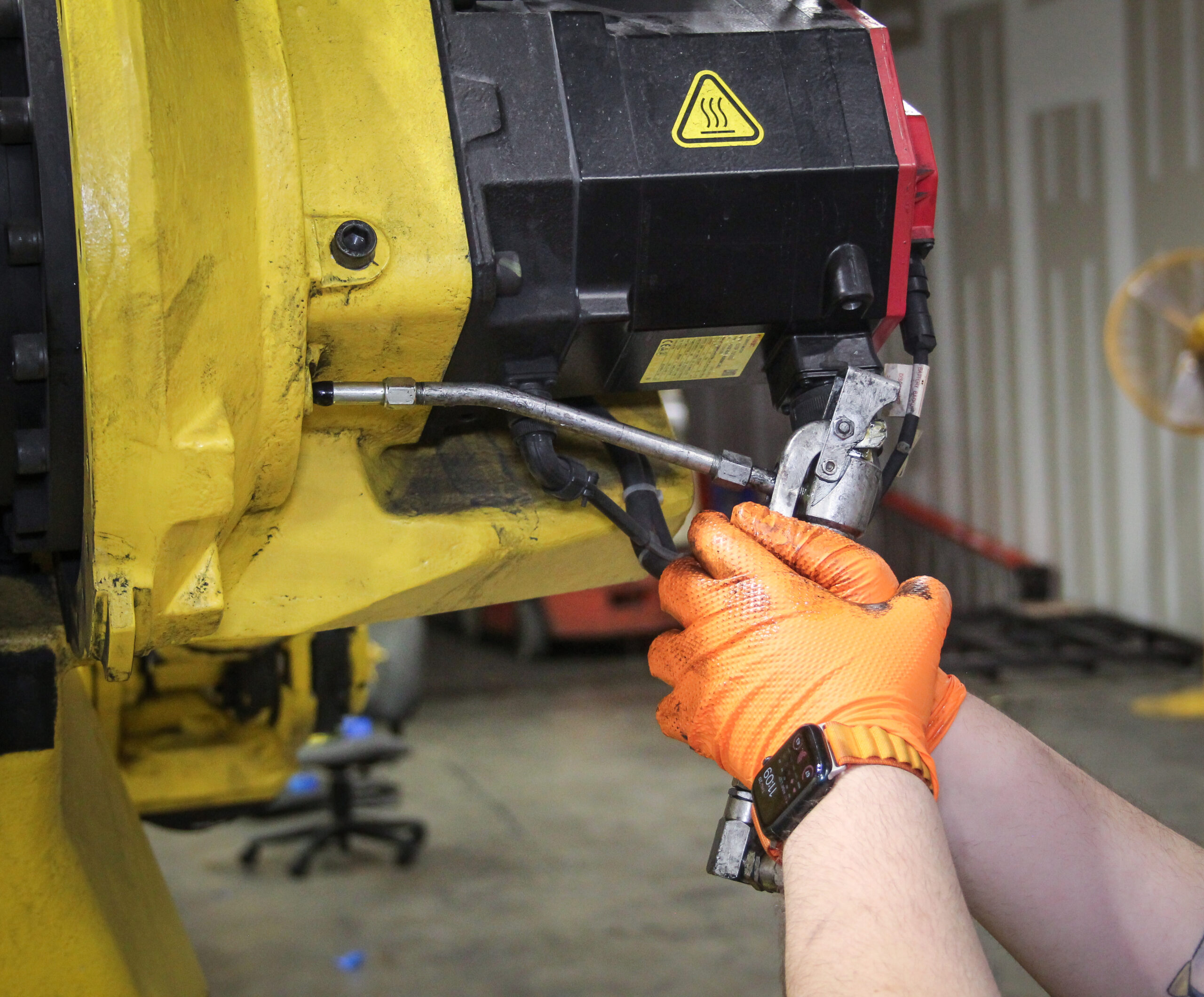
Proper lubrication is essential for keeping industrial robots running smoothly and efficiently. Robot grease is critical in reducing wear and tear, preventing overheating, and extending the lifespan of robotic components. Without regular and proper lubrication as part of a comprehensive industrial robot maintenance program, robots are prone to robot grease failures, leading to costly robot repairs and unexpected downtime.
This guide provides a step-by-step process for correctly greasing robot joints and gears. We’ll cover the necessary tools, best practices, and common mistakes to avoid, ensuring your robot remains in peak operating condition.
Table of Contents
- Why Proper Robot Lubrication Matters
- How Often Should You Grease Your Robot?
- Signs That Your Robot Is Due for Lubrication
- Tools and Materials Needed for Greasing Robot Joints
- Greasing Your Robot’s Joints and Gears Step by Step
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Greasing Robot Joints
- Best Practices for Long-Term Industrial Robot Maintenance
- Keep Your Robots Running Smoothly with T.I.E. Industrial
- Frequently Asked Questions About Greasing Robot Joints
Why Proper Robot Lubrication Matters
Before we detail how to grease robot joints, it’s essential to discuss why this is so essential. Industrial robots operate under extreme conditions, making robot maintenance a critical task for manufacturing professionals. High-speed movement, continuous operation, and exposure to dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations put significant stress on robotic components. Regular lubrication ensures:
- Reduced friction and wear on moving parts, helping to maintain precision and efficiency in robotic movements.
- Prevention of overheating and excessive energy consumption, which can otherwise lead to costly repairs and reduced operational efficiency.
- Minimized risk of contamination and corrosion, protecting sensitive internal components from environmental hazards.
- Increased operational efficiency and extended lifespan of robotic systems, ultimately reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Incorrect or neglected lubrication can lead to robot grease failures, causing premature component wear, unexpected breakdowns, and expensive robot repairs.
How Often Should You Grease Your Robot?
The recommended grease interval varies by manufacturer, model, and workload. Below is a breakdown of manufacturer-recommended lubrication schedules:
- Standard models: Grease replacement every 3,850 hours.
- High-duty cycle robots: May require more frequent lubrication.
ABB Robots
- General lubrication cycle: Every 5,000 – 10,000 hours.
- Gear lubrication checks: Recommended every six months.
KUKA Robots
- Yearly grease replenishment required for planetary gear reduction units.
- Semi-annual inspections of grease levels help detect early wear or leaks.
Motoman Robots
- High-speed models: May require more frequent lubrication.
- Grease replacement interval: Every 3,000 – 5,000 hours.
Signs That Your Robot Is Due for Lubrication
Even with a carefully documented industrial robot maintenance program, you may find your robots needing grease. If a robot is overdue for lubrication, it will show performance issues. Warning signs include:
- Abnormal noises such as grinding or squeaking during movement.
- Resistance or sluggish motion in robotic joints.
- Overheating in gearboxes or motor areas.
- Visible grease contamination, including dried-out residue, leaks, or dirt buildup.
Ignoring these signs can lead to severe mechanical failures and increased downtime.
Tools and Materials Needed for Greasing Robot Joints
Before you start greasing your robot joints, gather the following essential tools and materials:
- Manufacturer-recommended robot grease (varies by brand and model).
- Grease gun with compatible lubrication fittings.
- Lint-free cloths to wipe excess grease and prevent contamination.
- Maintenance logs or robot maintenance checklists to track lubrication schedules.
- Safety gloves and eye protection.
- A clean and dry workspace to prevent dirt and debris from contaminating the grease or lubrication points.
- A set of torque wrenches or other tools to remove protective covers, if necessary.
- Disposal containers or absorbent pads to handle excess grease and prevent spills.
- A flashlight or inspection light to check lubrication points for proper application and signs of wear.
Using the wrong type of grease can damage internal components. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications, such as those available at FanucWorld.

Greasing Your Robot’s Joints and Gears Step by Step
Follow this process for greasing your robot’s joints and gears:
Step 1: Review the Manufacturer’s Guidelines
Different robot brands have unique lubrication requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s maintenance manual to determine:
- The correct type of robot grease for your specific model.
- The frequency of lubrication cycles.
- Recommended application methods.
Step 2: Inspect the Robot Before Lubrication
Before applying grease, conduct a visual inspection of the robot:
- Look for signs of leaks, contamination, or dried-out grease.
- Check for excessive dirt or debris in lubrication points.
- Review maintenance logs to ensure the robot is due for lubrication.
- Use a robot maintenance checklist to keep track of inspections. A great resource is this ultimate checklist.
Step 3: Choose the Right Grease
Not all greases are created equal. The wrong lubricant can cause component degradation. Consider:
- Base oil viscosity: Higher viscosity greases are needed for high-load applications.
- Additive compatibility: Some greases contain anti-wear or anti-corrosion additives that improve durability.
- Temperature resistance: Ensure the grease can handle the robot’s operating environment, especially in high-temperature or moisture-prone areas.
- Shear stability: Some greases maintain their properties better under mechanical stress, reducing breakdown over time.
Step 4: Apply the Grease Correctly
Follow these best practices when applying grease:
- Use the right amount: Over-greasing can be just as harmful as under-greasing. Too much grease can cause excess heat buildup and attract contaminants.
- Apply steady pressure with the grease gun to avoid excess buildup.
- Lubricate in recommended intervals: Following manufacturer guidelines ensures consistency and prevents excessive wear.
- Rotate or move joints slightly while greasing to help distribute the lubricant evenly across the contact surfaces.
Step 5: Check for Excess Grease and Clean Up
After applying grease:
- Wipe away any excess to prevent dirt accumulation and contamination.
- Inspect for leaks or misplaced lubrication to ensure grease is applied correctly.
- Ensure lubrication points are contaminant-free by checking for dirt, metal shavings, or debris that could enter joints.
- Dispose of used grease materials properly by following workplace safety protocols for handling lubricants.
Step 6: Run a Test Cycle
Once you’ve finished greasing the robot’s joints:
- Power up the robot and run a test cycle to ensure smooth movement and even grease distribution.
- Listen for unusual noises or resistance that may indicate improper lubrication or an underlying issue.
- Check for leaks or displacement of grease around joints and moving parts.
- Document the maintenance process in maintenance logs for future reference.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Greasing Robot Joints
Greasing robot joints is not without pitfalls. Avoid these common mistakes to prevent costly robot repairs:
- Using the wrong grease type → Leads to component failure and breakdown.
- Skipping regular lubrication → Causes premature wear and increases downtime.
- Over-greasing → Traps contaminants, creates pressure buildup and can lead to overheating.
- Ignoring contamination risks → Dust and debris mixed with grease accelerate damage to moving parts.
- Not keeping maintenance records → Leads to inconsistent lubrication schedules and missed maintenance intervals.
Best Practices for Long-Term Industrial Robot Maintenance
Beyond greasing robot joints, ensure the longevity of your robotic systems by following these industrial robot maintenance tips:
- Follow a preventive maintenance schedule to address wear before failures occur.
- Conduct regular inspections to identify potential issues early.
- Keep spare parts on hand for quick robot repairs and minimal downtime.
- Train maintenance personnel on proper lubrication and robot upkeep procedures.
- Use high-quality lubricants recommended by the manufacturer to maintain efficiency and reduce component wear.
For high-quality robot grease, spare parts, and maintenance support, visit FanucWorld. Our extensive inventory of refurbished robotic systems and replacement parts ensures your robots operate efficiently with minimal downtime.
Keep Your Robots Running Smoothly with T.I.E. Industrial
If you need high-quality refurbished robots, robot replacement parts, or expert maintenance advice, T.I.E. Industrial has you covered. With an extensive inventory of refurbished robotic systems and replacement parts for leading robot brands, we help you keep your automation processes running smoothly.
Explore our selection of refurbished robots and parts today at T.I.E. Industrial.
Frequently Asked Questions About Greasing Robot Joints
It’s not unusual to have questions about greasing robot joints and gears. Below are answers to common questions that can help extend the life and performance of your industrial robot.
How often should I inspect seals and boots on robot joints?
You should visually inspect seals and boots every three to six months for signs of cracking, tearing, or grease leakage. Damaged seals can allow contaminants in or grease out, compromising internal components.
What kind of grease contamination should I look out for?
Watch for signs of metal shavings, water, or discoloration in old grease. These contaminants suggest gear wear, seal failure, or water ingress and may require a more in-depth inspection.
Is there a way to tell if the robot has been undergreased without opening it up?
You might notice increased joint noise, inconsistent motion, or higher-than-normal current draw. While not definitive, these can indicate insufficient lubrication and warrant further inspection.
Does ambient temperature affect the type of grease I should use?
Yes. Some greases are designed for high-heat environments, while others maintain better consistency in cold settings. Always check the robot manufacturer’s grease specifications for your operating conditions.
Was this helpful?
0 / 0